长江口及其邻近海域CDOM的光学特性研究
本文主要针对长江口地区不同季节有色可溶性有机物 (CDOM, Colored Dissolved Organic Matter) 光学特性进行研究,探讨了CDOM吸收特性的时空变化及其影响因素,并建立了CDOM光学特性与水体表层溶解有机碳浓度(DOC, Dissolved Organic Carbon)之间的经验关系。相较于传统的实地测量方法,利用DOC和CDOM光学特性之间的关系可以用遥感手段大范围同步观测长江口地区的DOC浓度,因而能够更直观的展示水体中DOC的变化和迁移,对于研究区域碳循环及物质迁移具有更高的适用价值。此外,文中也发现了在长江口近岸地区水体盐度和CDOM吸收系数有稳定的负相关关系,因此也使得利用水色遥感卫星反演长江口水体盐度成为可能,为研究长江口地区盐度分布以及盐水入侵等热门课题提供另一种选择。
Fig. 1. Location of sampling stations in the Changjiang estuarine and coastal waters. Samples were collected from five cruises in summer (July 2011, July 2012 and August 2013) and winter (February and March of 2012).
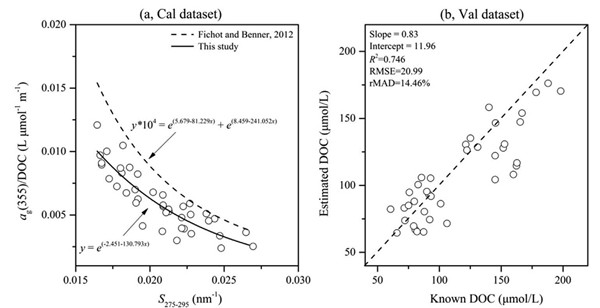
Fig. 7. Calibration and validation for DOC estimation model using the Cal and Val datasets. (a) A non-linear relationship (black line) is used to fit a*g(335) and S275-295 using the Cal dataset. A referential relationship from Fichot and Benner (2012) is also provided (dash line). (b) Validation of the developed model using the Val dataset.
相关成果在Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science上发表,全文见:
-
Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science ,
2016 ,
181
: 302-311